Cells of the Nervous System
Note to students: The best preparation for taking the reading quiz is to pay close attention to the key terms as you read. Each question in the question banks is directly linked to these key terms and phrases.
Chapter Focus Question:
How does the human nervous system transmit and process information from the environment, and why is this significant to the field of psychology?
- Nerve types
- Neurons
- Soma
- Information processing
- Terminal buttons
- Axon
- Myelin sheath
- MS
- Synapse
- Neurotransmitters
Section Focus Question:
What are the building blocks of the nervous system, and how are they scaffolded to provide a sensory relay system for the human body?
Key Terms:
Psychologists striving to understand the human mind may study the nervous system. Learning how the cells and organs (like the brain) function, helps us understand the biological basis behind human psychology. The nervous system is composed of two basic cell types: glial cells (also known as glia) and neurons. Glial cells, which outnumber neurons 10 to one, are traditionally thought to play a supportive role to neurons, both physically and metabolically. Glial cells provide scaffolding on which the nervous system is built, help neurons line up closely with each other to allow neuronal communication, provide insulation to neurons, transport nutrients and waste products, and mediate immune responses. Neurons, on the other hand, serve as interconnected information processors that are essential for all of the tasks of the nervous system. This section briefly describes the structure and function of neurons.
Neuron Structure
Neurons are the central building blocks of the nervous system, 100 billion strong at birth. Like all cells, neurons consist of several different parts, each serving a specialized function. A neuron’s outer surface is made up of a semipermeable membrane. This membrane allows smaller molecules and molecules without an electrical charge to pass through it, while stopping larger or highly charged molecules.
The nucleus of the neuron is located in the soma, or cell body. The soma has branching extensions known as dendrites. The neuron is a small information processor, and dendrites serve as input sites where signals are received from other neurons. These signals are transmitted electrically across the soma and down a major extension from the soma known as the axon, which ends at multiple terminal buttons. The terminal buttons contain synaptic vesicles that house neurotransmitters, the chemical messengers of the nervous system.
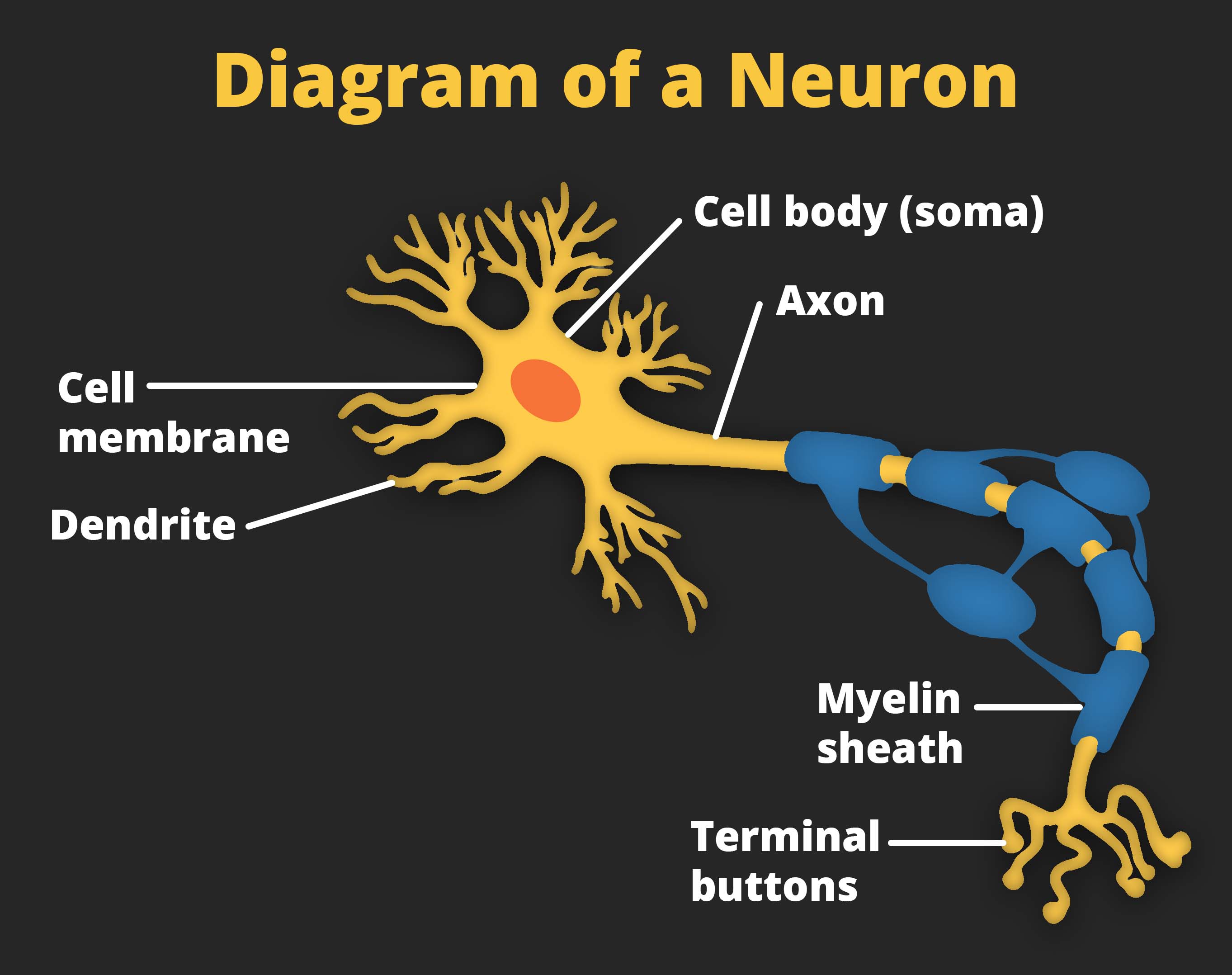
Axons range in length from a fraction of an inch to several feet. In some axons, glial cells form a fatty substance known as the myelin sheath, which coats the axon and acts as an insulator, increasing the speed at which the signal travels. The myelin sheath is crucial for the normal operation of the neurons within the nervous system: the loss of the insulation it provides can be detrimental to normal function. To understand how this works, let’s consider an example. Multiple sclerosis (MS), an autoimmune disorder, involves a large-scale loss of the myelin sheath on axons throughout the nervous system. The resulting interference in the electrical signal prevents the quick transmittal of information by neurons and can lead to a number of symptoms, such as dizziness, fatigue, loss of motor control, and sexual dysfunction. While some treatments may help to modify the course of the disease and manage certain symptoms, there is currently no known cure for multiple sclerosis.
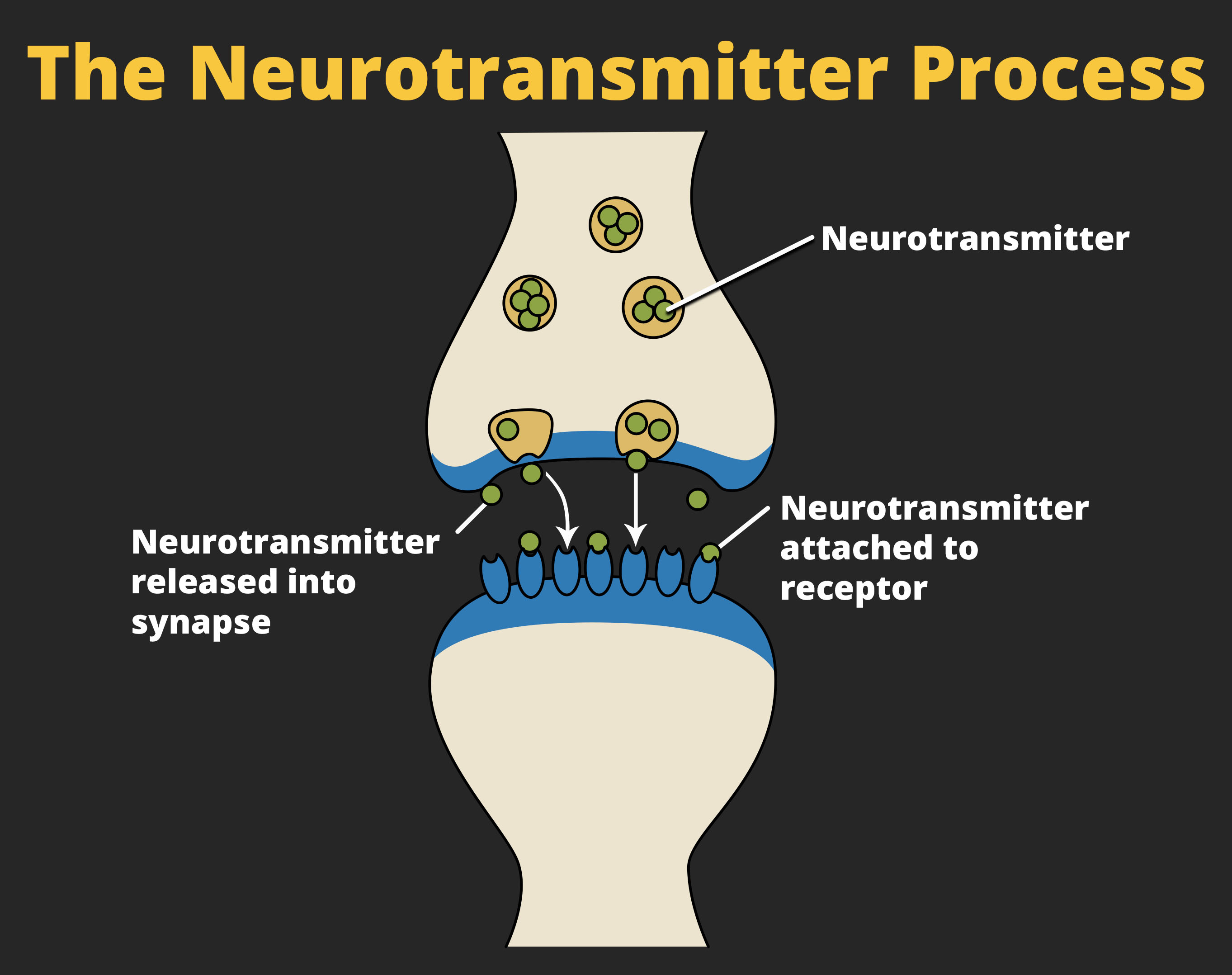
In healthy individuals, the neuronal signal moves rapidly down the axon to the terminal buttons, where synaptic vesicles release neurotransmitters into the synapse. The synapse is a very small space between two neurons and is an important site where communication between neurons occurs. Once neurotransmitters are released into the synapse, they travel across the small space and bind with corresponding receptors on the dendrite of an adjacent neuron. Receptors, proteins on the cell surface where neurotransmitters attach, vary in shape, with different shapes “matching” different neurotransmitters.
How does a neurotransmitter “know” which receptor to bind to? The neurotransmitter and the receptor have what is referred to as a lock-and-key relationship — specific neurotransmitters fit specific receptors similar to how a key fits a lock. The neurotransmitter binds to any receptor that it fits.
Neuronal Communication
- Cell membrane
- Membrane potential
- Ions
- Transmission of information
- Sodium and potassium
- Charged ions and movement
- Charge in the neuron
- Action potential
- Reaching the threshold of excitation
- Action potential spike
Section Focus Question:
How are impulses moved along the nervous system, and what role does electrical charge play?
Key Terms:
Now that we have learned about the basic structures of the neuron and the role that these structures play in neuronal communication, let’s take a closer look at the signal itself — how it moves through the neuron and then jumps to the next neuron, where the process is repeated.
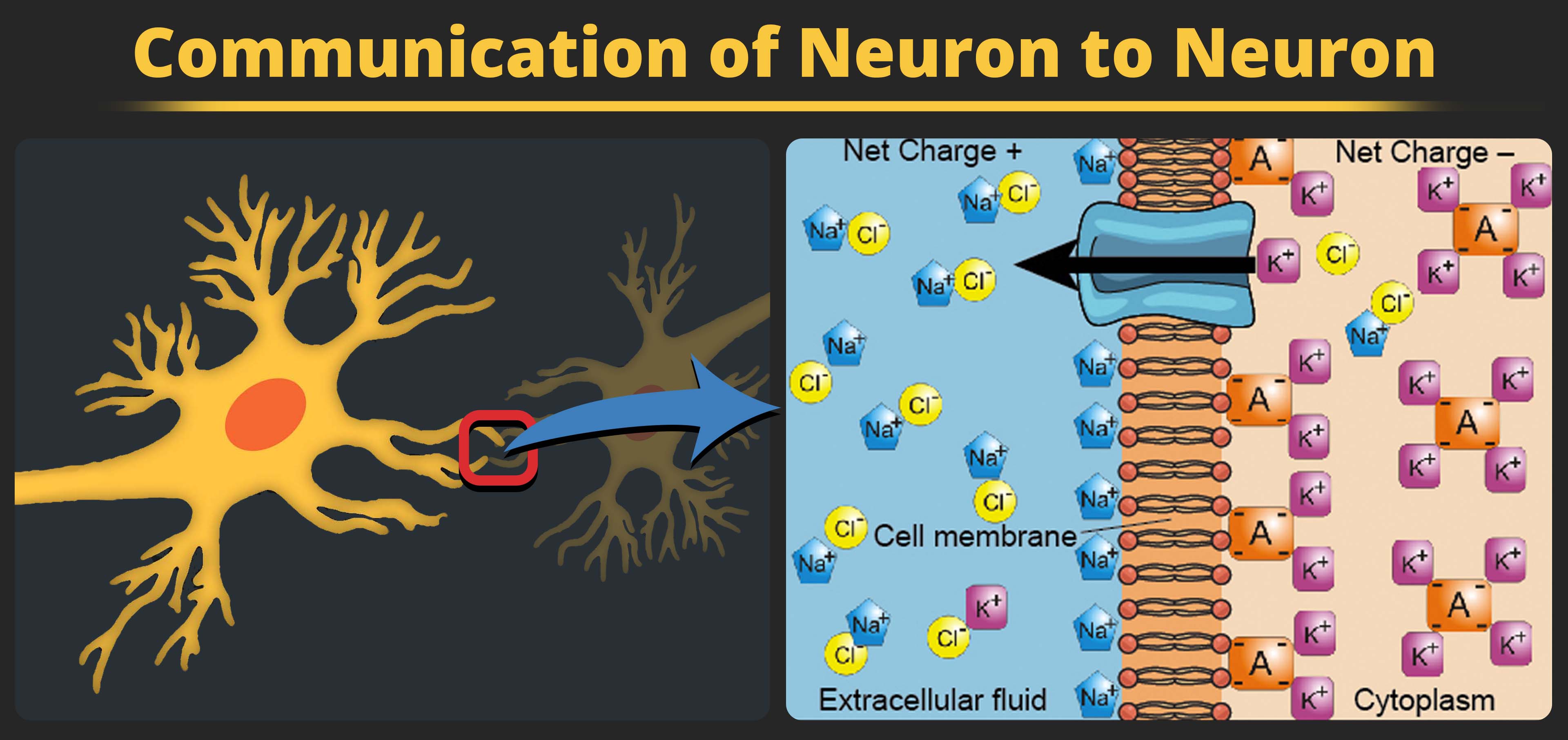
We begin at the neuronal membrane. The neuron exists in a fluid environment — it is surrounded by extracellular fluid and contains intracellular fluid (i.e., cytoplasm). The neuronal membrane keeps these two fluids separate — a critical role because the electrical signal that passes through the neuron depends on the intra- and extracellular fluids being electrically different. This difference in charge across the membrane, called the membrane potential, provides energy for the signal.
The electrical charge of the fluids is caused by charged molecules (ions) dissolved in the fluid. The semipermeable nature of the neuronal membrane somewhat restricts the movement of these charged molecules, and, as a result, some of the charged particles tend to become more concentrated either inside or outside the cell.
Between signals, the neuron membrane’s potential is held in a state of readiness, called the resting potential. Like a rubber band stretched out and waiting to spring into action, ions line up on either side of the cell membrane, ready to rush across the membrane when the neuron goes active and the membrane opens its gates (i.e., a sodium-potassium pump that allows movement of ions across the membrane). Ions in high-concentration areas are ready to move to low-concentration areas, and positive ions are ready to move to areas with a negative charge.
In the resting state, sodium (Na+) is at higher concentrations outside the cell, so it will tend to move into the cell. Potassium (K+), on the other hand, is more concentrated inside the cell, and will tend to move out of the cell. In addition, the inside of the cell is slightly negatively charged compared to the outside. This provides an additional force on sodium, causing it to move into the cell.
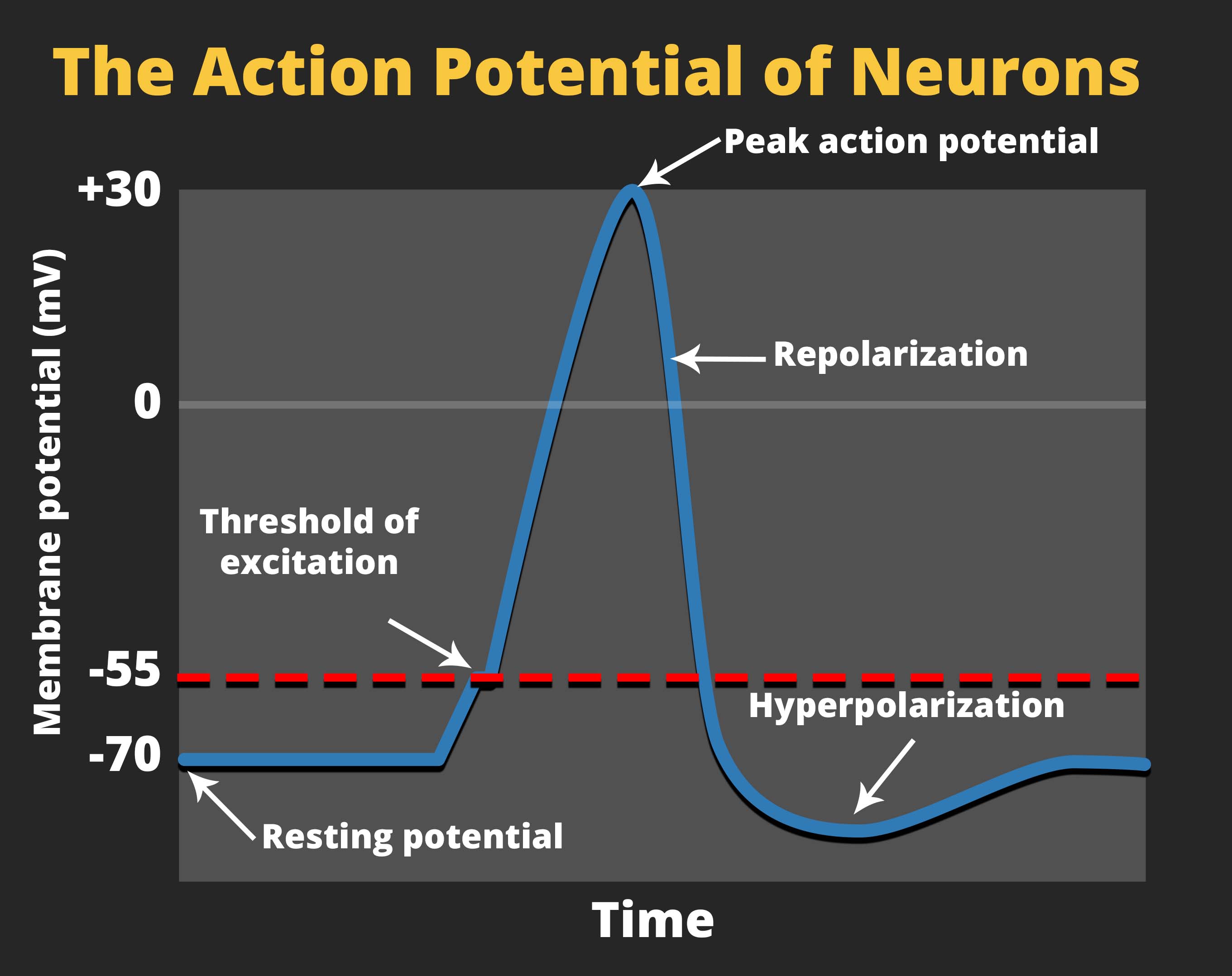
From this state of resting potential, the neuron receives a signal and its state changes abruptly. When a neuron receives signals at the dendrites — due to neurotransmitters from an adjacent neuron binding to its receptors — small pores, or gates, open on the neuronal membrane, allowing Na+ ions, propelled by both charge and concentration differences, to move into the cell. With this influx of positive ions, the internal charge of the cell becomes more positive. If that charge reaches the level referred to as the threshold of excitation, the neuron becomes active and the action potential begins.
Many additional pores open, causing a massive influx of Na+ ions and a huge positive spike in the membrane potential, the peak action potential. At the peak of the spike, the sodium gates close and the potassium gates open. As positively charged potassium ions leave, the cell quickly begins repolarization. At first, it hyperpolarizes, becoming slightly more negative than the resting potential, and then it levels off, returning to the resting potential.
This positive spike constitutes the action potential: the electrical signal that typically moves from the cell body down the axon to the axon terminals. The electrical signal moves down the axon like a wave; at each point, some of the sodium ions that enter the cell diffuse to the next section of the axon, raising the charge past the threshold of excitation and triggering a new influx of sodium ions. The action potential moves all the way down the axon to the terminal buttons.
- Propagation of action potential
- All-or-none property
- Reuptake
- Clearing the synapse
- Electrical nature of the action potential
- Chemical nature of neuronal communication
- Agonist effect
- Antagonist effect
- Opioids
- SSRIs/serotonin
Section Focus Question:
What purpose does reuptake serve, and how are drugs used to continue or block this process?
Key Terms:
The action potential is an all-or-none phenomenon. In simple terms, this means that an incoming signal from another neuron is either sufficient or insufficient to reach the threshold of excitation. There is no in-between, and there is no turning off an action potential once it starts. Think of it like sending an email or a text message. You can think about sending it all you want, but the message is not sent until you hit the send button. Furthermore, once you send the message, there is no stopping it.
Because it is all or none, the action potential is recreated, or propagated, at its full strength at every point along the axon. Much like the lit fuse of a firecracker, it does not fade away as it travels down the axon. It is this all-or-none property that explains the fact that your brain perceives an injury to a distant body part like your toe as equally painful as one to your nose.
As noted earlier, when the action potential arrives at the terminal button, the synaptic vesicles release their neurotransmitters into the synapse. The neurotransmitters travel across the synapse and bind to receptors on the dendrites of the adjacent neuron, and the process repeats itself in the new neuron (assuming the signal is sufficiently strong to trigger an action potential). Once the signal is delivered, excess neurotransmitters in the synapse drift away, are broken down into inactive fragments, or are reabsorbed in a process known as reuptake. Reuptake involves the neurotransmitter being pumped back into the neuron that released it, in order to clear the synapse. Clearing the synapse serves both to provide a clear “on” and “off” state between signals and to regulate the production of neurotransmitter (full synaptic vesicles provide signals that no additional neurotransmitters need to be produced).
Neuronal communication is often referred to as an electrochemical event. The movement of the action potential down the length of the axon is an electrical event, and movement of the neurotransmitter across the synaptic space represents the chemical portion of the process.